Register now or log in to join your professional community.

A

a carburetor mixes the air with the fuel to mixture that is inserted or injected into the cylinders, so A and C

A SI engines, Spark-Ignition engines

I would have said A, but than I checked what a CI engine is and what a carburetor does so I came to the conclusion that SI and CI are combustion motors and both can use corroborators .. so A and C is my answer
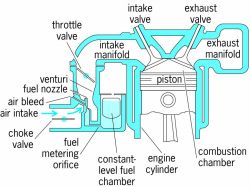
A device that controls the power output and fuel feed of internal combustion spark-ignition engines used for automotive, aircraft, and auxiliary services. Its duties include control of the engine power by the air throttle; metering, delivery, and mixing of fuel in the air stream; and graduating the fuel-air ratio according to engine requirements in starting, idling, and load and altitude changes. The fuel is usually gasoline or similar liquid hydrocarbon compounds,although some engines with a carburetor may also operate on a gaseous fuel such as propane or compressed natural gas. A carburetor may be classified as having either a fixed venturi, in which the diameter of the air opening ahead of the throttle valve remains constant, or a variable venturi, which changesarea to meet the changing demand. See Automobile, Engine, Fuel system, Venturi tube
A simple updraft carburetor with a fixed venturi illustrates basic carburetor action (see illustration). Intake air charge, at full or reduced atmosphericpressure as controlled by the throttle, is drawn into the cylinder by the downward motion of the piston to mix with the unscavenged exhaust remaining inthe cylinder from the previous combustion. A cylinder is most completely filled with the fuel-air mixture when no other cylinder is drawing in through the same intake passage at the same time. The fuel is usually metered through a calibrated orifice, or jet, at a differential pressure derived from the pressure drop in a venturi in the intake air passage.