Register now or log in to join your professional community.

By using Radio Data System (RDS) which is a communications protocol standard for embedding small amounts of digital information in conventional FM radio broadcasts. RDS standardizes several types of information transmitted, including time, station identification and program information.
FM band (87.5 to 108 MHz).
FM stereo multiplex bandwidth is about 100 kHz.
RDS Frequency: 57 kHz within the FM stereo multiplex.

In FM signal transmit though transmitter and it will be modulated and after receiver it will again demodulated.

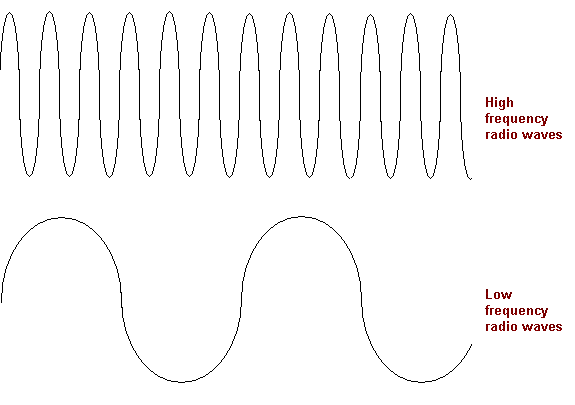
There are two common ways to put information in a radio wave, and you've likely run into them yourself. They are called A.M. and F.M. just like the two choices you've always known are on a radio. To understand these two ways of sending information it is important to know that radio waves, by themselves, have very regular patterns. Generally they keep the same amplitude or frequency all the time. (Amplitude is the "height" of the radio wave, frequency is how close the waves are to each other.)
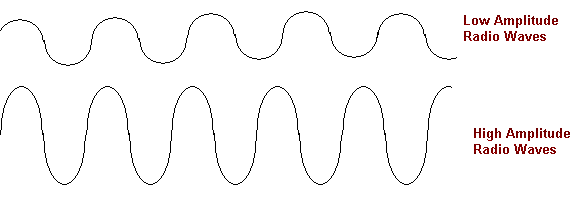
A.M. stands for amplitude modulation. In this method, the information is put into a radio wave by varying the amplitude. For example, if all we wanted to do was send1's and0's, we could have just two different levels of amplitude that correspond to these numbers--1 being high,0 being low.

F.M. stands for frequency modulation. This time the amplitude is kept constant, it is the frequency that is varied..
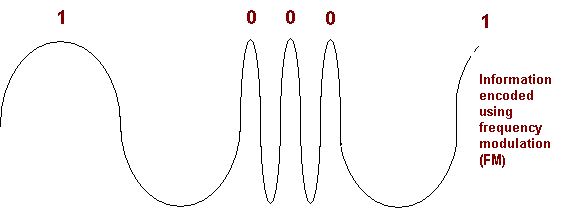

the FM multiplexed signal bandwidth is KHZ and you can send data in side FM signal by RDS. signal and at frequency KHZ

FM band is from ( -) MHz . The FM stations are assigned center frequencies at kHz separation starting at.1 MHz, for a maximum of stations. These FM stations have a kHz maximum deviation from the center frequency, which leaves kHz upper and lower "gaurd bands" to minimize interaction with the adjacent frequency band.



