Register now or log in to join your professional community.

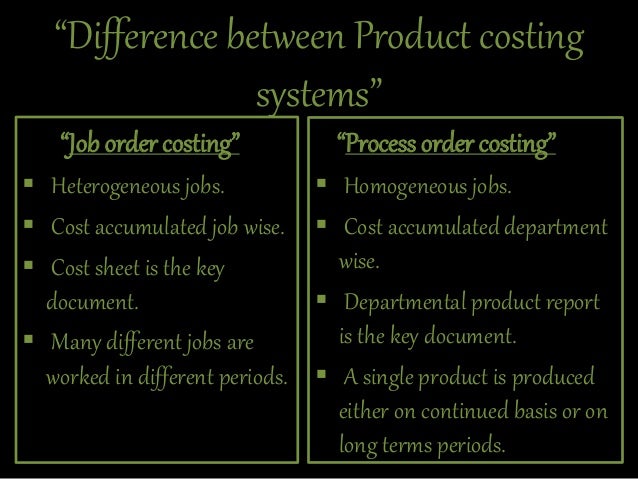
Job Costing basically refers to the costs that are encountered in the businesses related to manufacturing goods. Job Costing ledgers, wherein such costs are recorded, form an integral part of the final account statement of the manufacturers. This type of costing involves recording the costs as per the specific jobs rather than a particular process. However, Process Costing refers to the methodology involved in calculating the costs that are incurred while performing a particular task or undertaking a specific process. This might involve the costs that are either incurred directly or indirectly.
Job Costing involves the costs of every individual unit of production. However, Process Costing involves the costs that are averaged for each production unit. As per the definition, Process Costing is a method that is applied to the manufacture business that is held together by various continuous or repetitive processes. Process Costing works efficiently for the industries that are known to produce a single type of product. Both of these terms signify the costs related to labor, material and overhead costs.
Process Costing helps to keep a tight reign over the monthly expenditures in a manufacturing business. As an example, Job Costing involves the costs that form salaries of labors working in a particular process whereas Process Costing involves the costs of the processed or manufactured goods undertaken by different departments.
One of the major differences between Job Costing and Process Costing is that the Job Costing can be carried out while a particular job is going on. However, Process Costing can be achieved only when all the processes are completed. Moreover, when it comes to documentation, in case of Job Costing, the job cost sheet is important whereas in Process Costing a document having deposition and accumulation of various costs is important.
In summary, there are various differences between Job Costing and Process Costing methods. Some of these are listed below:
1. Job Costing signifies the costs encountered for each and every job whereas Process Costing signifies the costs encountered for different departments.
2. In case of Job Costing, a final value of the costs can be calculated beforehand whereas in Process Costing, the final value of the costs is calculated only at the end of the complete process.
3. The important documents needed to carry out Job Costing are much different from those needed for Process Costing.
4. Job Costing is typically used by industries that manufacture customized and heterogenous products whereas Process Costing method is used by the industries that are involved in mass production of homogenous products.

Job costing involves the detailed accumulation of production costs attributable to specific units or groups of units. For example, the construction of a custom-designed piece of furniture would be accounted for with a job costing system. The costs of all labor worked on that specific item of furniture would be recorded on a time sheet and then compiled on a cost sheet for that job. Similarly, any wood or other parts used in the construction of the furniture would be charged to the production job linked to that piece of furniture. This information may then be used to bill the customer for work performed and materials used, or to track the extent of the company's profits on the production job associated with that specific item of furniture.
Process costing involves the accumulation of costs for lengthy production runs involving products that are indistinguishable from each other. For example, the production of 100,000 gallons of gasoline would require that all oil used in the process, as well as all labor in the refinery facility be accumulated into a cost account, and then divided by the number of units produced to arrive at the cost per unit. Costs are likely to be accumulated at the department level, and no lower within the organization.
Given these descriptions of job costing and process costing, we can arrive at the following differences between the two costing methodologies:
In situations where a company has a mixed production system that produces in large quantities but then customizes the finished product prior to shipment, it is possible to use elements of both the job costing and process costing systems, which is known as ahybrid system.
Job costing and process costing can be used in both manual and computerized accounting environments.