Register now or log in to join your professional community.
What is CSS3 transitions, and how it work?

Css3 transition make smooth animation when changing style of element from another style without using any js animation.

CSS3 transitions are effects that let an element change from one style to another.

You can use also animate.css http://daneden.me/animate/, a good javascript framework based on css3

Using CSS transition you can apply the transition effect on an element that change style to style, You don't need to use javascript or jquery for applying transition effect however if you want to apply advnce transition efffect & more interactive transition effect your best bet is jquery.
There are few parameter you can set for transition like transition property, duration, easing, delay. Almost all mordern browser support css transition but if some browser not support then you can use vender specific prefix like -webkit- (chrome ver), -o- (ver of opera), -moz- (for ver of fiexfox).

CSS3 Transitions are a presentational effect which allow property changes in CSS values, such as those that may be defined to occur on :hover or :focus, to occur smoothly over a specified duration – rather than happening instantaneously as is the normal behaviour.
Transition effects can be applied to a wide variety of CSS properties, including background-color,width, height, opacity, and many more. Keep reading for further details of supported properties.
The CSS3 Transitions module introduces a number of properties which together can be used to specify: the CSS property (or properties) to be transitioned; the duration of the transition; the timing function of the transition; and an optional delay.
These properties are as follows:
The module also introduces the transition shorthand property, which can be used to set the values for the above four properties simultaneously.
We will firstly look at the individual transition-* properties to demonstrate how each works, before going on to look at the shorthand syntax.
The first step in creating a transition effect is to specify which CSS property (or properties) the transition effect will be applied to. This can be done using the transition-property property, which can accept one of two keywords, all (the initial value) or none, or a comma-separated list of properties.
The Syntax: transition-property: none | all | [ <IDENT> ] [, <IDENT> ]*
Examples: transition-property: all;transition-property: none;transition-property: background-color;transition-property: background-color, height, width;
If the all keyword is specified, or if transition-property is omitted, every property that is able to undergo a transition will do so, ie. every property for which a change has been specified and that is capable of supporting transitions.
If the none keyword is specified, no property will undergo a transition.
As with multiple background images, multiple transitions can be specified using a comma separated list. If multiple values are specified for transition-property, multiple values should also be specified for the other transition-* properties, with the corresponding values in each list being matched in order.
A full list of animatable CSS properties, ie. those that are able to undergo a transition, can be foundhere in section6 of the CSS3 Transitions specification.
The transition-duration property accepts a comma-separated list of times, specified in seconds or milliseconds, which determine how long the corresponding properties (specified using transition-property) take to complete their transition.
The Syntax: transition-duration: <time> [, <time>]*
Examples: transition-duration:2s;transition-duration:4000ms;transition-duration:4000ms,8000ms;
The transition-duration property's initial value is0, meaning that the transition is instantaneous.
Negative values for transition-duration are treated as0.
Note: The transition-duration property is in fact the only property required to create a transition effect, as if transition-property is not supplied, all properties that are able to undergo a transition will do so.
The transition-timing-function property is used to specify how the pace of the transition changes over its duration. This can be done in one of two ways. Either by specifying a number of pre-defined keywords (ease, linear, ease-in, ease-out or ease-in-out), or by defining a custom timing function (by specifying four coordinates to define a cubic bezier curve).
The Syntax: transition-timing-function: <timing-function> [, <timing-function>]*
<timing-function> = ease | linear | ease-in | ease-out | ease-in-out
or
<timing-function> = cubic-bezier(<number>, <number>, <number>, <number>)
Examples: transition-timing-function: ease;transition-timing-function: ease, linear;transition-timing-function: cubic-bezier(0.6,0.1,0.15,0.8);
Let's first take a look at the pre-defined timing functions available.
The example below demonstrates how each different function behaves. Each box below will expand in width from150px to500px when the example is hovered over, with all transitions being of the same duration (3 seconds) and triggered simultaneously.
ease linear ease-in ease-out ease-in-out
The code for this example can be found in the examples section below.
In addition to the pre-defined timing functions, custom timing functions can be declared using thecubic-bezier function. According to the specification:
The timing function is specified using a cubic bezier curve, which is defined by four control points, P0 through P3 (see diagram below). P0 and P3 are always set to (0,0) and (1,1). The ‘transition-timing-function’ property is used to specify the values for points P1 and P2. These can be set to preset values using the keywords listed (see above), or can be set to specific values using the ‘cubic-bezier’ function. In the ‘cubic-bezier’ function, P1 and P2 are each specified by both an X and Y value.
Diagram: Timing Function Control Points
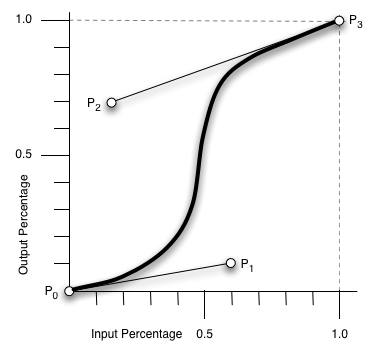
If you're not familiar with cubic bezier curves, more information on defining custom timing functions can be found in section2.3 of the CSS3 Transitions specification here.
If no timing function is specified, the default value is ease.
The final step in a creating a transition effect is to specify an optional delay using the transition-delay property. As with the transition-duration property, the transition-delay property accepts a comma-separated list of times, specified in seconds or milliseconds, which in this case determines the length of time between the transition being triggered and the transition starting. The default value is0, ie. the transition will commence as soon as triggered.
Negative values are accepted for transition-delay. When supplied the transition will commence as soon as triggered, however it will appear to have begun execution at the specified offset, ie; the transition effect will begin part-way through its cycle (see the examples section below for an example).
The Syntax: transition-delay: <time> [, <time>]*
Examples: transition-delay:5s;transition-delay:4000ms,8000ms;transition-delay: -5s;
The transition shorthand property can be used in place of the individual transition-* properties described above.
Let's take a look at the syntax.
The Syntax: transition: <transition> [, <transition>]*
<transition> = <transition-property> <transition-duration> <transition-timing-function> <transition-delay>
As with the individual transition-* properties, the transition shorthand property can be used to define multiple transitions, using a comma separated list.
Note: The only value required to create a transition is that of transition-duration.
Examples: transition: background-color3s linear1s;transition:4s ease-in-out;transition:5s;
CSS3 transitions properties are used to animate smoothly from the old state to the new state over time.
Types are:
transitions-property,
transitions-duration,
transitions-timing-function,
transitions-delay.



