Register now or log in to join your professional community.

The Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming API for HTML and XML documents. It defines the logical structure of documents and the way a document is accessed and manipulated. In the DOM specification, the term "document" is used in the broad sense - increasingly, XML is being used as a way of representing many different kinds of information that may be stored in diverse systems, and much of this would traditionally be seen as data rather than as documents. Nevertheless, XML presents this data as documents, and the DOM may be used to manage this data.
With the Document Object Model, programmers can create and build documents, navigate their structure, and add, modify, or delete elements and content. Anything found in an HTML or XML document can be accessed, changed, deleted, or added using the Document Object Model, with a few exceptions - in particular, the DOM interfaces for the internal subset and external subset have not yet been specified.
As a W3C specification, one important objective for the Document Object Model is to provide a standard programming interface that can be used in a wide variety of environments and applications. The Document Object Model can be used with any programming language. In order to provide precise, language-independent specification of the Document Object Model interfaces, we have chosen to define the specifications in OMG IDL, as defined in the CORBA 2.2 specification. In addition to the OMG IDL specification, we provide language bindings for Java and ECMAScript (an industry-standard scripting language based on JavaScript and JScript). Note: OMG IDL is used only as a language-independent and implementation-neutral way to specify interfaces. Various other IDLs could have been used; the use of OMG IDL does not imply a requirement to use a specific object binding runtime.

DOM defines a platform-neutral model for events and node trees.
Here's the structure of HTML DOM given in w3cschools. This diagram helps us to easily understand the structure of a web page.
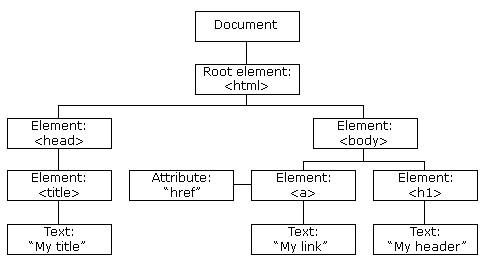

In the Document Object Model, documents have a logical structure which is like a "forest" which can contain more than one tree

The Document Object Model (DOM) is an application programming interface (API) for valid HTML and well-formed XML documents. It defines the logical structure of documents and the way a document is accessed and manipulated.

Document Object Model (DOM) is a programming interface for HTML and XML documents. It provides a structured representation of the document and it defines a way that the structure can be accessed from programs so that they can change the document structure, style and content. The DOM provides a representation of the document as a structured group of nodes and objects that have properties and methods. Essentially, it connects web pages to scripts or programming languages.
A Web page is a document. This document can be either displayed in the browser window, or as the HTML source. But it is the same document in both cases. The Document Object Model (DOM) provides another way to represent, store and manipulate that same document. The DOM is a fully object-oriented representation of the web page, and it can be modified with a scripting language such as JavaScript.

Thank you for the invitation
The DOM is a W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) standard. The DOM defines a standard for accessing documents: "The W3C Document Object Model (DOM) is a platform and language-neutral interface that allows programs and scripts to dynamically access and update the content, structure, and style of a document.".


