Register now or log in to join your professional community.

There are two ways to incorporate the graph in Excel via keyboard shortcuts:
The first way: the inclusion of a graph on the same sheet (Alt + F1).
The second way: the inclusion of a graph on a separate sheet (F11).

To insert a new sheet in the workbook, with a chart for the selected data, you can press the F11 key.

To insert the chart on the active worksheet, use the Alt + F1 shortcut keys

When you create a chart using the keyboard shortcuts, the default chart type is used. To select a different default chart type:
On the Excel Ribbon, click the Insert tab
In the Charts group, click the Dialog Launcher button, at the bottom right

Select one of the chart types, and a Sub-type, then click Set as Default Chart

Click Cancel, to close the window.
Then, when you create new charts with one of the keyboard shortcuts, the new default type will be used.

I fully agree with the answer been added by MR Vinod Jetley ..........................Thanks.

1. To insert a new sheet in the workbook, with a chart for the selected data, you can press the F11 key.
2. To insert the chart on the active worksheet, use the Alt + F1

............ALT + F1 or F11

I agree with the answers given already and voted them up for F11 and Alt F1

SELECT THE RANG THEN PRESS F11

Shortcut key alt+shift+F1....................

You have two options:
Option1: Chart Sheet. F11
this will inset new worksheet with only a chart called chart sheet.
Option2: Alt+F1
this will insert a chart object in the active worksheet for the selected data.
Hope this helps you

I learnt something new today thanks for every body

If you're new to the ribbon, the information in this section can help you understand the ribbon's keyboard shortcut model. The ribbon comes with new shortcuts, called Key Tips. To make the Key Tips appear, press Alt.
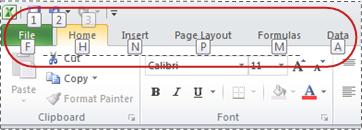
To display a tab on the ribbon, press the key for the tab—for example, press the letter N for the Insert tab or M for the Formulas tab. This makes all the Key Tip badges for that tab's buttons appear. Then, press the key for the button you want.
Keyboard shortcuts that begin with Ctrl will still work in Microsoft Excel 2013. For example, Ctrl+C still copies to the clipboard, and Ctrl+V still pastes from the clipboard.
Most of the old Alt+ menu shortcuts still work, too. However, you need to know the full shortcut from memory — there are no screen reminders of what letters to press. For example, try pressing Alt, and then press one of the old menu keys E (Edit), V (View), I (Insert), and so on. A box pops up saying you're using an access key from an earlier version of Microsoft Office. If you know the entire key sequence, go ahead and initiate the command. If you don't know the sequence, press Esc and use Key Tip badges instead.
Ctrl combination shortcut keysKey
Description
Ctrl+PgDn
Switches between worksheet tabs, from left-to-right.
Ctrl+PgUp
Switches between worksheet tabs, from right-to-left.
Ctrl+Shift+&
Applies the outline border to the selected cells.
Ctrl+Shift_
Removes the outline border from the selected cells.
Ctrl+Shift+~
Applies the General number format.
Ctrl+Shift+$
Applies the Currency format with two decimal places (negative numbers in parentheses).
Ctrl+Shift+%
Applies the Percentage format with no decimal places.
Ctrl+Shift+^
Applies the Scientific number format with two decimal places.
Ctrl+Shift+#
Applies the Date format with the day, month, and year.
Ctrl+Shift+@
Applies the Time format with the hour and minute, and AM or PM.
Ctrl+Shift+!
Applies the Number format with two decimal places, thousands separator, and minus sign (-) for negative values.
Ctrl+Shift+*
Selects the current region around the active cell (the data area enclosed by blank rows and blank columns).
In a PivotTable, it selects the entire PivotTable report.
Ctrl+Shift+:
Enters the current time.
Ctrl+Shift+"
Copies the value from the cell above the active cell into the cell or the Formula Bar.
Ctrl+Shift+Plus (+)
Displays the Insert dialog box to insert blank cells.
Ctrl+Minus (-)
Displays the Delete dialog box to delete the selected cells.
Ctrl+;
Enters the current date.
Ctrl+`
Alternates between displaying cell values and displaying formulas in the worksheet.
Ctrl+'
Copies a formula from the cell above the active cell into the cell or the Formula Bar.
Ctrl+1
Displays the Format Cells dialog box.
Ctrl+2
Applies or removes bold formatting.
Ctrl+3
Applies or removes italic formatting.
Ctrl+4
Applies or removes underlining.
Ctrl+5
Applies or removes strikethrough.
Ctrl+6
Alternates between hiding and displaying objects.
Ctrl+8
Displays or hides the outline symbols.
Ctrl+9
Hides the selected rows.
Ctrl+0
Hides the selected columns.
Ctrl+A
Selects the entire worksheet.
If the worksheet contains data, Ctrl+A selects the current region. Pressing Ctrl+A a second time selects the entire worksheet.
When the insertion point is to the right of a function name in a formula, displays the Function Arguments dialog box.
Ctrl+Shift+A inserts the argument names and parentheses when the insertion point is to the right of a function name in a formula.
Ctrl+B
Applies or removes bold formatting.
Ctrl+C
Copies the selected cells.
Ctrl+D
Uses the Fill Down command to copy the contents and format of the topmost cell of a selected range into the cells below.
Ctrl+E
Adds more values to the active column by using data surrounding that column.
Ctrl+F
Displays the Find and Replace dialog box, with the Find tab selected.
Shift+F5 also displays this tab, while Shift+F4 repeats the last Find action.
Ctrl+Shift+F opens the Format Cells dialog box with the Font tab selected.
Ctrl+G
Displays the Go To dialog box.
F5 also displays this dialog box.
Ctrl+H
Displays the Find and Replace dialog box, with the Replace tab selected.
Ctrl+I
Applies or removes italic formatting.
Ctrl+K
Displays the Insert Hyperlink dialog box for new hyperlinks or the Edit Hyperlink dialog box for selected existing hyperlinks.
Ctrl+L
Displays the Create Table dialog box.
Ctrl+N
Creates a new, blank workbook.
Ctrl+O
Displays the Open dialog box to open or find a file.
Ctrl+Shift+O selects all cells that contain comments.
Ctrl+P
Displays the Print tab in Microsoft Office Backstage view.
Ctrl+Shift+P opens the Format Cells dialog box with the Font tab selected.
Ctrl+Q
Displays the Quick Analysis options for your data when you have cells that contain that data selected.
Ctrl+R
Uses the Fill Right command to copy the contents and format of the leftmost cell of a selected range into the cells to the right.
Ctrl+S
Saves the active file with its current file name, location, and file format.
Ctrl+T
Displays the Create Table dialog box.
Ctrl+U
Applies or removes underlining.
Ctrl+Shift+U switches between expanding and collapsing of the formula bar.
Ctrl+V
Inserts the contents of the Clipboard at the insertion point and replaces any selection. Available only after you have cut or copied an object, text, or cell contents.
Ctrl+Alt+V displays the Paste Special dialog box. Available only after you have cut or copied an object, text, or cell contents on a worksheet or in another program.
Ctrl+W
Closes the selected workbook window.
Ctrl+X
Cuts the selected cells.
Ctrl+Y
Repeats the last command or action, if possible.
Ctrl+Z
Uses the Undo command to reverse the last command or to delete the last entry that you typed.
Tip: The Ctrl combinations Ctrl+J and Ctrl+M are currently unassigned shortcuts.
Function keysKey
Description
F1
Displays the Excel Help task pane.
Ctrl+F1 displays or hides the ribbon.
Alt+F1 creates an embedded chart of the data in the current range.
Alt+Shift+F1 inserts a new worksheet.
F2
Edits the active cell and positions the insertion point at the end of the cell contents. It also moves the insertion point into the Formula Bar when editing in a cell is turned off.
Shift+F2 adds or edits a cell comment.
Ctrl+F2 displays the print preview area on the Print tab in the Backstage view.
F3
Displays the Paste Name dialog box. Available only if names have been defined in the workbook (Formulas tab, Defined Names group, Define Name).
Shift+F3 displays the Insert Function dialog box.
F4
Repeats the last command or action, if possible.
When a cell reference or range is selected in a formula, F4 cycles through all the various combinations of absolute and relative references.
Ctrl+F4 closes the selected workbook window.
Alt+F4 closes Excel.
F5
Displays the Go To dialog box.
Ctrl+F5 restores the window size of the selected workbook window.
F6
Switches between the worksheet, ribbon, task pane, and Zoom controls. In a worksheet that has been split (View menu, Manage This Window, Freeze Panes, Split Window command), F6 includes the split panes when switching between panes and the ribbon area.
Shift+F6 switches between the worksheet, Zoom controls, task pane, and ribbon.
Ctrl+F6 switches to the next workbook window when more than one workbook window is open.
F7
Displays the Spelling dialog box to check spelling in the active worksheet or selected range.
Ctrl+F7 performs the Move command on the workbook window when it is not maximized. Use the arrow keys to move the window, and when finished press Enter, or Esc to cancel.
F8
Turns extend mode on or off. In extend mode, Extended Selection appears in the status line, and the arrow keys extend the selection.
Shift+F8 enables you to add a nonadjacent cell or range to a selection of cells by using the arrow keys.
Ctrl+F8 performs the Size command (on the Control menu for the workbook window) when a workbook is not maximized.
Alt+F8 displays the Macro dialog box to create, run, edit, or delete a macro.
F9
Calculates all worksheets in all open workbooks.
Shift+F9 calculates the active worksheet.
Ctrl+Alt+F9 calculates all worksheets in all open workbooks, regardless of whether they have changed since the last calculation.
Ctrl+Alt+Shift+F9 rechecks dependent formulas, and then calculates all cells in all open workbooks, including cells not marked as needing to be calculated.
Ctrl+F9 minimizes a workbook window to an icon.
F10
Turns key tips on or off. (Pressing Alt does the same thing.)
Shift+F10 displays the shortcut menu for a selected item.
Alt+Shift+F10 displays the menu or message for an Error Checking button.
Ctrl+F10 maximizes or restores the selected workbook window.
F11
Creates a chart of the data in the current range in a separate Chart sheet.
Shift+F11 inserts a new worksheet.
Alt+F11 opens the Microsoft Visual Basic For Applications Editor, in which you can create a macro by using Visual Basic for Applications (VBA).
F12
Displays the Save As dialog box.
Other useful shortcut keysKey
Description
Alt
Displays the Key Tips (new shortcuts) on the ribbon.
For example,
Alt, W, P switches the worksheet to Page Layout view.
Alt, W, L switches the worksheet to Normal view.
Alt, W, I switches the worksheet to Page Break Preview view.
Arrow Keys
Move one cell up, down, left, or right in a worksheet.
Ctrl+Arrow Key moves to the edge of the current data region in a worksheet.
Shift+Arrow Key extends the selection of cells by one cell.
Ctrl+Shift+Arrow Key extends the selection of cells to the last nonblank cell in the same column or row as the active cell, or if the next cell is blank, extends the selection to the next nonblank cell.
Left Arrow or Right Arrow selects the tab to the left or right when the ribbon is selected. When a submenu is open or selected, these arrow keys switch between the main menu and the submenu. When a ribbon tab is selected, these keys navigate the tab buttons.
Down Arrow or Up Arrow selects the next or previous command when a menu or submenu is open. When a ribbon tab is selected, these keys navigate up or down the tab group.
In a dialog box, arrow keys move between options in an open drop-down list, or between options in a group of options.
Down Arrow or Alt+Down Arrow opens a selected drop-down list.
Backspace
Deletes one character to the left in the Formula Bar.
Also clears the content of the active cell.
In cell editing mode, it deletes the character to the left of the insertion point.
Delete
Removes the cell contents (data and formulas) from selected cells without affecting cell formats or comments.
In cell editing mode, it deletes the character to the right of the insertion point.
End
End turns End mode on or off. In End mode, you can press an arrow key to move to the next nonblank cell in the same column or row as the active cell. End mode turns off automatically after pressing the arrow key. Make sure to press End again before pressing the next arrow key. End mode is shown in the status bar when it is on.
If the cells are blank, pressing End followed by an arrow key moves to the last cell in the row or column.
End also selects the last command on the menu when a menu or submenu is visible.
Ctrl+End moves to the last cell on a worksheet, to the lowest used row of the rightmost used column. If the cursor is in the formula bar, Ctrl+End moves the cursor to the end of the text.
Ctrl+Shift+End extends the selection of cells to the last used cell on the worksheet (lower-right corner). If the cursor is in the formula bar, Ctrl+Shift+End selects all text in the formula bar from the cursor position to the end—this does not affect the height of the formula bar.
Enter
Completes a cell entry from the cell or the Formula Bar, and selects the cell below (by default).
In a data form, it moves to the first field in the next record.
Opens a selected menu (press F10 to activate the menu bar) or performs the action for a selected command.
In a dialog box, it performs the action for the default command button in the dialog box (the button with the bold outline, often the OK button).
Alt+Enter starts a new line in the same cell.
Ctrl+Enter fills the selected cell range with the current entry.
Shift+Enter completes a cell entry and selects the cell above.
Esc
Cancels an entry in the cell or Formula Bar.
Closes an open menu or submenu, dialog box, or message window.
It also closes full screen mode when this mode has been applied, and returns to normal screen mode to display the ribbon and status bar again.
Home
Moves to the beginning of a row in a worksheet.
Moves to the cell in the upper-left corner of the window when Scroll Lock is turned on.
Selects the first command on the menu when a menu or submenu is visible.
Ctrl+Home moves to the beginning of a worksheet.
Ctrl+Shift+Home extends the selection of cells to the beginning of the worksheet.
Page Down
Moves one screen down in a worksheet.
Alt+Page Down moves one screen to the right in a worksheet.
Ctrl+Page Down moves to the next sheet in a workbook.
Ctrl+Shift+Page Down selects the current and next sheet in a workbook.
Page Up
Moves one screen up in a worksheet.
Alt+Page Up moves one screen to the left in a worksheet.
Ctrl+Page Up moves to the previous sheet in a workbook.
Ctrl+Shift+Page Up selects the current and previous sheet in a workbook.
Spacebar
In a dialog box, performs the action for the selected button, or selects or clears a check box.
Ctrl+Spacebar selects an entire column in a worksheet.
Shift+Spacebar selects an entire row in a worksheet.
Ctrl+Shift+Spacebar selects the entire worksheet.
If the worksheet contains data, Ctrl+Shift+Spacebar selects the current region. Pressing Ctrl+Shift+Spacebar a second time selects the current region and its summary rows. Pressing Ctrl+Shift+Spacebar a third time selects the entire worksheet.
When an object is selected, Ctrl+Shift+Spacebar selects all objects on a worksheet.
Alt+Spacebar displays the Control menu for the Excel window.
Tab
Moves one cell to the right in a worksheet.
Moves between unlocked cells in a protected worksheet.
Moves to the next option or option group in a dialog box.
Shift+Tab moves to the previous cell in a worksheet or the previous option in a dialog box.
Ctrl+Tab switches to the next tab in dialog box.
Ctrl+Shift+Tab switches to the previous tab in a dialog box.



