Register now or log in to join your professional community.

Hybrids are vehicles that combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor as the power source. Add a sophisticated transmission and powerful batteries and it's a recipe that makes the most of gasoline, the one fuel that's available in all fifty states--at more than180,000 stations. Hybrids utilize the electric motor and battery storage to maximize the fuel economy from standard gasoline-burning engines. Depending upon the design and usage, hybrids can boast up to30 percent fuel savings (sometimes more) over a comparable gasoline vehicle. And that translates into less greenhouse gases spewed into the environment also. Best of all, hybrids are designed for ease of use just hop in and go.

Have you pulled your car up to the gas pump lately and been shocked by the high price of gasoline? As the pump clicked past $20, $30, $40 or even $50, maybe you thought about trading in your car for something that gets better mileage. Or maybe you're worried that your car is contributing to the greenhouse effect.
The auto industry has the technology to address these concerns. It's the hybrid car. There are a lot of hybrid models on the market these days, and most automobile manufacturers have announced plans to manufacture their own versions.
How does a hybrid automobile work? What goes on under the hood to give you20 or30 more miles per gallon than the standard automobile? And does it pollute less just because it gets better gas mileage? In this article, we'll help you understand how this technology works, and we'll even give you some tips on how to drive a hybrid car for maximum efficiency.
Hybrid vehicles are called hybrids because they use both a small internal combustion engine (ICE) and an electric motor to obtain maximum power and fuel economy with minimum emissions. How they do this varies from one model to another, with varying success.
What all hybrids have in common is the ability to generate electric current, store it in a large battery, and use that current to help drive the car. Hybrids capture electrical energy produced by a regenerative braking system, and their engines can power a generator, too. Hybrids can also conserve energy by shutting down the ICE when the vehicle is in Park, idling at a light, or stopped in traffic, or when the electric motor’s energy is sufficient to drive the vehicle without assistance from the ICE.
Hybrids have regenerative braking systems that generate electric power to help keep the batteries charged. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor turns into a generator, and the magnetic drag slows the vehicle down. For safety, however, there is also a normal hydraulic braking system that can stop the car when regenerative braking isn’t sufficient. There’s no difference in maintenance or repair except that the brake pads tend to last much longer because they don’t get used as much. In fact, if you drive a hybrid in a moderate manner, you almost never actually use the disc brakes on the wheels and may be able to go the life of the car without changing pads. The big difference is that regenerative brakes capture energy and turn it into electricity to charge the battery that provides power to an electric motor.
Parallel hybridsA parallel hybrid uses both an electric motor and an ICE for propulsion. They can run in tandem, or one can be used as the primary power source with the other kicking in to assist when extra power is needed for starting off, climbing hills, and accelerating to pass other vehicles. Because both are connected to the drive train, they’re said to run “in parallel.”
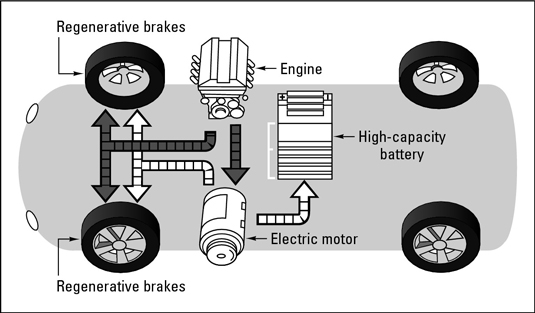 How a parallel hybrid works.
Series hybrids
How a parallel hybrid works.
Series hybrids
A series hybrid uses a gasoline or diesel ICE, coupled with a generator, to generate electricity but not to drive the car. The engine can send the electric current directly to the electric motor or charge a large battery that stores the electricity and delivers it to an electric motor on-demand. The electric motor propels the vehicle, using its power to rotate a driveshaft or a set of drive axles that turn the wheels.
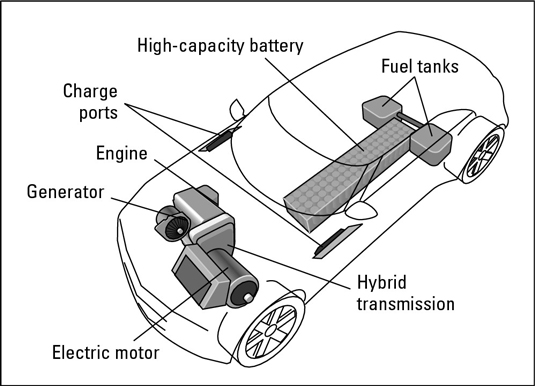 A series hybrid.
Plug-in hybrids
A series hybrid.
Plug-in hybrids
Because plug-in hybrids feature larger batteries that can be charged at any ordinary110-volt electrical socket, they have the capacity to extend the ability of the electric motor to drive the car farther without the need for starting the ICE and therefore substantially increase the vehicle’s fuel efficiency. Estimates have ranged as high as100 mpg!
Some technologically savvy individuals have adapted their hybrid vehicles into plug-in hybrids, and automakers are in the process of developing and producing them (sometimes in cooperation with major utility companies). The development of new, smaller, high-capacity lithium-ion batteries that can be recharged many times is the key to making plug-in hybrids available to the general public. Estimates are that plug-in hybrids equipped with these more powerful batteries will have a range of as much as125 miles before the charge is depleted and the vehicle reverts to standard hybrid mode.
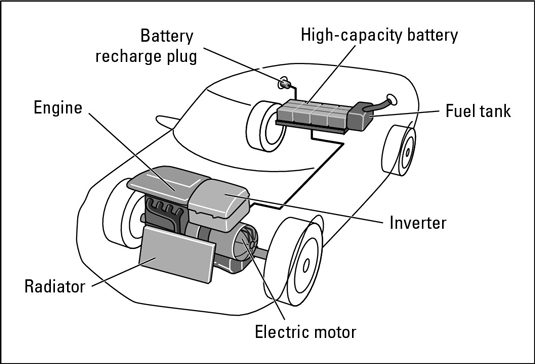 A plug-in hybrid.
A plug-in hybrid.
The main environmental problem with plug-in hybrids is that the electric current they draw is usually generated by utility companies powered by fossil fuels. The good news is that some major chains have committed to establishing charging stations powered by solar panels or wind energy, and many hybrid owners are willing to install solar panels to recharge these vehicles at home. Plug-in hybrids charged by commercial sources of electricity or solar panels will be less dependent on the ICE, but will still need it for long trips, climbing hills, and so on. Future hybrids may use a small fuel cell to make electricity from hydrogen, which would mean the ICE would have to run even less frequently.
Two-mode hybridsTwo-mode hybrids may be the key to a competitive place for the U.S. in the hybrid market. Instead of the large storage battery found on conventional hybrids, two-mode hybrids use smaller batteries and two electric motors located inside an automatic transmission with two sets of gears — one for the ICE and the other to amplify the power of the electric motors. The transmission can function as a continuously variable transmission, as well. In one mode, at lower speeds, the vehicle can run with one or both electric motors, with or without the ICE, or on the ICE alone. At higher speeds, the second mode kicks in, and the ICE runs continuously in its higher gear ratios.
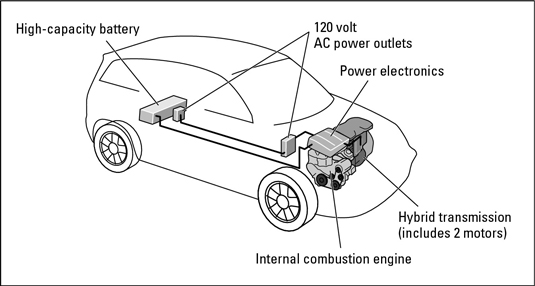 A two-mode hybrid.
A two-mode hybrid.
Many people have probably owned a hybrid vehicle at some point. For example, a mo-ped (a motorized pedal bike) is a type of hybrid because it combines the power of a gasoline engine with the pedal power of its rider. In fact, hybrid vehicles are all around us. Most of the locomotives we see pulling trains are diesel-electric hybrids. Cities like Seattle have diesel-electric buses -- these can draw electric power from overhead wires or run on diesel when they are away from the wires. Giant mining trucks are often diesel-electric hybrids. Submarines are also hybrid vehicles -- some are nuclear-electric and some are diesel-electric. Any vehicle that combines two or more sources of power that can directly or indirectly provide propulsion power is a hybrid. Most hybrid cars on the road right now are gasoline-electric hybrids, although French car maker PSA Peugeot Citroen has two diesel-electric hybrid cars in the works. Since gasoline hybrids are the kind you'll find at your local car dealership, we'll focus on those in this article.

Hybrids are vehicles that combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor as the power source. Add a sophisticated transmission and powerful batteries and it's a recipe that makes the most of gasoline, the one fuel that's available in all fifty states--at more than180,000 stations.
Mild
Full
Plug in

A petroleum-electric hybrid most commonly uses internal combustion engines (using a variety of fuels, generally gasoline or Diesel engines) and electric motors to power thevehicle. The energy is stored in the fuel of the internal combustion engine and an electric battery set.

motive power system operation vehicle. with the modern generation environment technology.


التعريف
تعبير هجين هو ترجمة لكلمة هيبريد Hybrid المشتقة من الكلمة اليونانية هيبريدا، والتي تعني خليط. ويدل استعمال كلمة هيبريد على تشارك عدد من عناصر معينة في تشكيل عملية واحدة.
[عدل]الاستعمال التقني
يدل وصف هجين تقنياً على استخدام نظام تقني متطور يجمع تقنيتين مختلفتين لتحقيق الهدف ، وهو حركة السيارة.
تعتمد السيارة الهجين على نظام حركي مؤلف من من نوعين مختلفين لتخزين الطاقة وتحويلها إلى حركة. على سبيل المثال، يتم استخدام محرك كهربائي إلى جانب محرك احتراق داخلي كطريقة لتحويل الطاقة إلى حركة ، وهي تستخدمبطارية كهربائية بالإضافة إلى وقود معتاد كطريقتين لتخزين الطاقة ثم تحويلها إلى طاقة حركة.
أثناء تشغيل السيارة يكون من الممكن استخدام كلا المحركين بشكل متتابع متواز أو منفصل عن بعضهما. فيقوم لمحرك الكهربائي بقطع المسافات الأولى على الطريق حيث تكون البطارية مشحونة بالكانل في أول القيادة . ولا ينتج عن ذلك غازات ضارة بالبيئة . وقرب نفاذ الطاقة الكهربية يبدأ محرك الاحتراق الداخلي عمله المعهود لمواصلة الطريق.
و غالبا ما يتم استعمال محرك احتراق داخلي إلى جانب بطارية كهربائية و مولد كهربائي ، و يعمل هذا الأخير على تخزين طاقة كهربائية في البطارية أثناء السير .
وتستند الحركة إلى تحويل قسم من طاقة الحركة المولّدة بواسطة محرك الاحتراق إلى بطارية المحرك الكهربائي بواسطة مولد كهربائي (دينامو) ويتم تخزينها في البطارية. ويمكن بعد ذلك استخدامها عند اللزوم كطاقة لتشغيل المحرك الكهربائي ، الذي بإمكانه تولّي دور المحرك العادي بشكل كلي في حالة السرعات المتوسطة.
تُجري مصانع السيارات بحوثا للتخفيف من حجم وثقل البطاريات المستعملة حاليا حيث تأخذ قدرا كبيرا من حمولة السيارة. كذلك تعمل على تطوير المحركات الكهربائية بحيث تنخفض الضوضاء الصادرة منها في السرعات العالية. وبالنسبة للبطارية الكهربائية فهناك التفكير في الاستعاضة عنها بوساطة تكنولوجيا جديدة تعمل بخلايا الوقود التي تعتمد على تفاعل الهيدروجين والأكسجين لتوليد الطاقة الكهربائية. ومن مزايا الخلايا الكهربائية التي تعمل بالهيدروجين أنها لا تنتج موادا ضارة بالبيئة أو سامة، وإنما العادم فيها عبارة عن
ماء.



