Register now or log in to join your professional community.

Thanks Ms GHada for invitation
1. Personnel management deals with employees, their payroll and employment laws. On the other hand, Human Resources Management deals with the management of the work force, and contributes to an organization’s success.
2. HRM basically deals with developing personnel management skills. It is Human Resources Management that develops a team of employees for an organization.
3. While Personnel management is considered to be reactive, Human Resources Management is stated to be proactive.
4. Personnel management focuses on administrating people or employees. On the other hand, the prime focus of Human Resources Development is to build a dynamic culture.
5. Personnel management is independent from an organization. On the contrary, Human Resources Management forms an integral part of a company or an organization.

Primarily, Personnel management is often considered an old-fashioned name for human resource management, and in some organizations there may well be little difference between the old personnel department and today’s HR department. But HRM can also mean a particular philosophy of the role of HRM in organizations, and how people are developed and nurtured to achieve organizational goals.
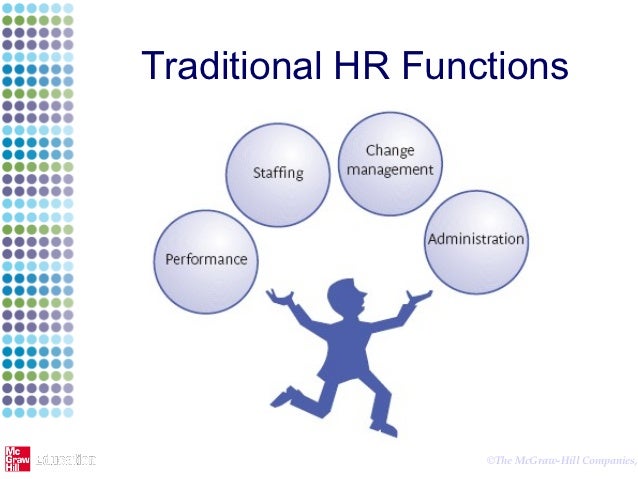
Distinguishing between HRM and PM
First of all Staffing objectives, Performance objectives, Change-management objectives and Administration objectives need to be taken into account, whether personnel management or HRM. However, personnel management is viewed as workforce centred and more operational in focus. Personnel managers recruit, select and carry out administrative procedures in accordance with management’s requirements. They act as a bridge between the employer and the employee. As a result, personnel managers were seen as functional specialists rather than strategic managers and often had little power or status in the organization. The personnel manager needed to understand the needs of the manager and the employee, and articulate those needs to both sides. Some organizations, however, see HRM as a particular approach in the management of people. HRM can be seen as a radical new approach linked to strategy and viewing people as assets who need to be actively managed as part of the long-term interests of the organization. HRM can be viewed as a radical integrated approach to the management of people in an organization and, as such, can be seen as a general management function. Where personnel managers can be viewed as specialists, HRM can be seen as the responsibility of all managers, particularly senior managers, and as such is proactive rather than reactive ( please refer to the table of comparison next)

in previous table , Guest (1987) identifies the differences in his model shows that HRM is commitment based, which is distinct from compliance-based personnel management. According to Guest, HRM is:
· linked to the strategic management of an organization
· seeks commitment to organizational goals
· focuses on the individual needs rather than the collective workforce.
· enables organizations to devolve power and become more flexible
· emphasizes people as an asset to be positively utilized by the organization.
Guest (1987) sees HRM as a distinct approach to managing the workforce and argues that, although personnel management will also select and train staff, it is the distinct approach in the selection and training that matters. HRM’s approach should be linked to high performance and commitment rather than compliance. Guest (1997) recognises that, although empirical evidence is only just beginning to show the link between HRM and performance, evidence is already suggesting that HRM works. The view from industry is also suggesting that HRM is taking on a strategic role in industry. The CIPD (2003) HR survey identified HR issues as now being regularly discussed at executive boards and HR managers seeing their role as that of a strategic business partner, with the HR function now focused on achieving key business goals and developing employee capabilities.
Storey defines the elements that differentiate HRM as follows:
· Human capability and commitment: Storey argues that this is what differentiates organizations.
· Strategic importance of HRM: it needs to be implemented into the organizational strategy and considered at the highest management level.
· The long-term importance of HRM: it needs to be integrated into the management functions and seen to have important consequences for the ability of the organization to achieve its goals.
· The key functions of HRM: seen to encourage commitment rather than compliance.
Storey (1992) identifies a model with 27 points that differentiate HRM from personnel and industrial relations (IR) practices ( please review the table next).

Storey’s model is based on an ideal type of organization andis a tool used to present what Storey sees as the essential features of personnel and HRM in an exaggerated way.
Storey’s model can be viewed as an ‘ideal type’ of HRM and has been used as a tool for research and analysis of organizations. In practice, HRM would use some elements of his 27 points but would be extremely unlikely to include all of them. As such the model is useful as a research tool but does not reflect what happens in practice (see the figure). Storey’s (1992) 27 points of difference identify personnel management as being bureaucratic, based on rules and procedures and seen as a separate function from general management. On the other hand, HRM is seen as related to the business need, and central to the corporate plan and the responsibility of all managers. Storey (1992) proposes another model as a means of comparative analysis, for identifying the shift organizations may take from personnel management to HRM.
Storey (1992) suggests in the model depicted in the model that, for an organization to gain competitive advantage, a strategic response needs to be given to the beliefs and assumptions of the organizations and that line managers should take on part of this role. Line managers would have a responsibility for the change in key levers, which would move the organization away from being locked into bureaucratic procedures towards becoming a flexible organization that would encourage commitment through performance-related goals.

Thanks for the invite ............................ agreed with the answers Mr. Vaiyapuri Gopalakrishnan

The main difference between personnel management and human resource management is that the former is the traditional approach the latter represents the modern approach toward managing people in an enterprise. This article will discuss the numerous differences between the two approaches.
How do you compare personnel management vs human resource management?
Significant difference exists between personnel management and human resource management in terms of scope, approach, and application.
Human Resource Management is broader in scope than Personnel Management.
The scope of personnel management includes functional activities such as manpower planning, recruitment, job analysis, job evaluation, payroll administration, performance appraisals, labor law compliance, training administration, and related tasks. Human resources management includes all these activities plus organizational developmental activities such as leadership, motivation, developing organizational culture, communication of shared values, and so forth.
The human resource management approach remains integrated to the company’s core strategy and vision. It seeks to optimize the use of human resources for the fulfillment of organizational goals. This strategic and philosophical context of human resource management makes it more purposeful, relevant, and more effective compared to the personnel management approach.
The personnel management approach tends to attach much importance to norms, customs and established practices, whereas the human resource approach gives importance to values and mission.
The personnel management approach also concerns itself with establishing rules, policies, procedures, and contracts, and strives to monitor and enforce compliance to such regulations, with careful delineation of written contract. The human resource management approach remains impatient with rules and regulations. HR managers tend to relax rules based on business needs and exigencies, and aim to go by the spirit of the contract rather than the letter of the contract.
An illustration of this difference in approach lies in the treatment of employee motivation. The personnel management approach holds employee satisfaction as the key to keeping employees motivated, and institutes compensation, bonuses, rewards, and work simplification initiatives as possible motivators. The human resource philosophy holds improved performance as the driver of employee satisfaction, and devises strategies such as work challenges, team work, and creativity to improve motivation.
Another dimension of the difference is the proactive nature of human resource management compared to the reactive nature of personnel management.
Personnel management remains aloof from core organizational activities, functions independently, and takes a reactive approach to changes in corporate goals or strategy. Human resource management remains integrated with corporate strategy and takes a proactive approach to align the workforce toward achievement of corporate goals.
For instance, while the personnel management approach concerns itself with a reactive performance appraisal process, human resource management approach has a more comprehensive and proactive performance management system that aims to correct performance rather than make a report card of past performance.
Personnel management is an independent staff function of an organization, with little involvement from line managers, and no linkage to the organization's core process. Human resource management, on the other hand, remains integrated with the organization's core strategy and functions. Although a distinct human resource department carries out much of the human resource management tasks, human resource initiatives involve the line management and operations staff heavily.
Personnel management also strives to reconcile the aspirations and views of the workforce with management interest by institutional means such as collective bargaining, trade union-based negotiations and similar processes. This leads to fixation of work conditions applicable for all, and not necessarily aligned to overall corporate goals.
Human Resource management gives greater thrust on dealing with each employee independently and gives more importance to customer-focused developmental activities and facilitating individual employees rather than bargaining or negotiating with trade unions.
Finally, in any discussion of personnel management vs human resource management, we must include that personnel management lays down rigid job description with many grades and a fixed promotion policy--usually based on seniority and performance appraisal ratings. Human resource management, on the other hand, has relatively fewer grades and ranks, with broadly defined job responsibilities providing much scope for applying creativity and initiative, and plenty of career paths, with skills, talent and commitment the key drivers of career advancement.

The Human Resource Management is a relatively new technique that designates what is called once the "Personnel Management".
The evolution of the denomination is significant in that it has swapped a negative connotation against a positive connotation.
The staff is pretty synonymous cost, while speaking to this resource ... an element that must take care of the way to make the most "favorable". In other words it is:
- Know find appropriate this resource,
- Know motivate and stimulate this resource,
- Know develop this resource.
These three basic missions of the Human ressources management must still be done respecting the environment. This appears mainly as a constraint in terms of:
- The legislative environment
- The economic environment,
- Technological environment,
- Socio-cultural environment.
The Hunaines Resources Management has taken gradually as the companies grew, a new weight. More different heavy environmental trends such as the globalization of markets, the Evolution technology, investment policies and the slowdown in growth, requires the management of human resources to evolve considerably.
The basic steps of the Human Resources Management are:
- Manage new employees (hiring procedures)
- Maintain exixtant staff (monitoring of employees in the company)
- Predict future skills needs of the company (forward management of human resources).
This is according to this order that are discussed chnologique human resources management tools.

I have nothing to add
Fantastic Answers
Mr. Ahmed
Mr. Najib

I fully agree and endorse the experts submissions here.
Thanx for the invtation

Human resource management is the new version of personnel management. There is no any watertight difference between human resource management and personnel management. However, there are some differences in the following matters. 1. Personnel management is a traditional approach of managing people in the organization. Human resource management is a modern approach of managing people and their strengths in the organization. 2. Personnel management focuses on personnel administration, employee welfare and labor relation. Human resource management focuses on acquisition, development, motivation and maintenance of human resources in the organization. 3. Personnel management assumes people as a input for achieving desired output. Human resource management assumes people as an important and valuable resource for achieving desired output. 4. Under personnel management, personnel function is undertaken for employee's satisfaction. Under human resource management, administrative function is undertaken for goal achievement. 5. Under personnel management, job design is done on the basis of division of labor. Under human resource management, job design function is done on the basis of group work/team work. 6. Under personnel management, employees are provided with less training and development opportunities. Under human resource management, employees are provided with more training and development opportunities. 7. In personnel management, decisions are made by the top management as per the rules and regulation of the organization. In human resource management, decisions are made collectively after considering employee's participation, authority, decentralization, competitive environment etc. 8. Personnel management focuses on increased production and satisfied employees. Human resource management focuses on effectiveness, culture, productivity and employee's participation. 9. Personnel management is concerned with personnel manager. Human resource management is concerned with all level of managers from top to bottom. 10. Personnel management is a routine function. Human resource management is a strategic function

I fully endorse Ghada's view.
My way of understanding is that HRM is evolved version of PM. Hence the Resource identified is nurtured and groomed too.

I prefer to leave answers to Experts. Thanks for Your kind Invitation.

Both the terms refer to the one and the same function of the management and that is managing the people at work.
However, Human Resource Management is mainly focussed on best utilising the man power by understanding their strength and weaknesses and engaging them in different occupations so that their productivity can be increased. Therefore, training and development and employee engagements are part of it.
Personnel Management, on the other hand, is mainly concerned with maintaining good employee- employer relationship and activities connected with it. Therefore, Personnel Management mainly works around Industrial/ Employee/ Labour Relations and activities connected with grievance handling, negotiations, enforcement of labour statute, looking after welfare of employees and so on.


