Register now or log in to join your professional community.

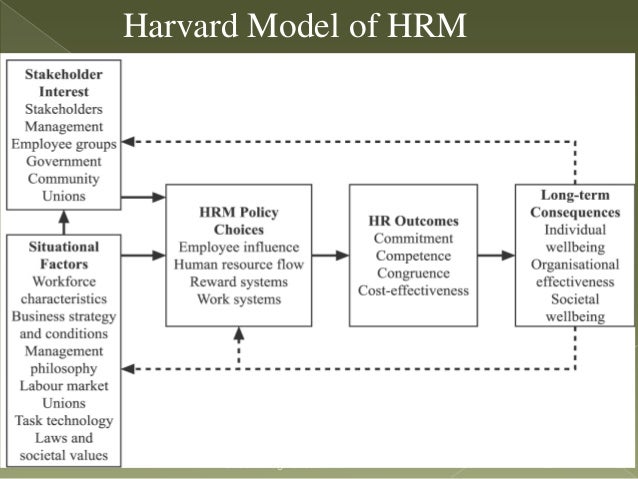
Figure The Harvard model of human resource management.
Source: (Beer et al 1984)
The Harvard model of HRMThe analytical framework of the 'Harvard model' offered by beer et al .consists six basic components:
1-Situation factors.
2-Stakeholder interests
3-HRM policy choices.
4-HR outcomes.
5-Long-term consequences
6-Feedback loop through which the output flow directly into the organisation and to the stakeholders
The implications of Harvard Model for HR manager in policy areas:
Which in turn lead to the 'four C's' or HR policies that have to be achieved:

Thanks
I agree with the answer given by colleague Shahul

The penalties for not being correctly staffed are costly. Planning staff levels requires that an assessment of present and future needs of the organization be compared with present resources and future predicted resources. Appropriate steps should then be planned to bring demand and supply into balance. The central aim of modern human resource management is to enhance the effective use, involvement and contribution of employees throughout the organization. This, clearly, requires a great deal of information accretion, classification and statistical analysis as a subsidiary aspect of personnel management. What future demands will be is only influenced in part by the forecast of the human resource manager, whose main task may well be to scrutinize and modify the crude predictions of other managers

A distinctive approach for managing human resources published by Richard Walton in an article in 1985 in the Harvard Business Review called ‘From Control to Commitment in the Workplace’. His argument was that effective HRM depends not on strategies for controlling employees but on strategies for winning employees’ commitment.
Many of the diverse personnel and labour relations activities can be dealt with under four human resource (HR) categories as proposed by the Harvard model, they are employee influence, human resource flow, reward systems and work systems. These are general issues that managers must attend to regardless of whether the organisation is unionised or not, whatever management style is applied, and whether it is a growing or declining business.
Employee influence is the question of how much responsibility, authority, and power is voluntarily delegated by management to the employees. The assumption the authors make is that any influence employees have should be compatible with management’s purpose and-priorities.
Managers and personnel specialists, according to the Harvard model, must work together to ensure that the organisation has an appropriate flow of people to meet its strategic requirements. Human resource flow concerns managing the flow of people into, through, and out of the organisation. This means making decisions on recruitment and selection, promotion, termination of employment, and related issues of job security, career development, advancement, and fair treatment.
Reward systems regulate how employees are extrinsically and intrinsically rewarded for their work. Extrinsic rewards are tangible pay and benefits: pay, overtime pay, bonuses, profit sharing, pensions, holiday entitlement, health insurance; and other benefits, such as flexible working hours. Intrinsic rewards are intangible benefits and are said to strongly influence employees’ motivation, job satisfaction, and organisational commitment. Intrinsic rewards are rewards from the work itself, such as sense of purpose, achievement, challenge, involvement, self-confidence, self-esteem, and satisfaction. The Harvard model recommends that employees should be highly involved in the design of an organisation’s reward systems but observes that final decisions, besides meeting employees’ needs, must be consistent with the overall business strategy, management philosophy, and other HRM policies.
Work systems are the ways in which people, information, activities, and technology are arranged, at all levels of the organisation, so that work can be performed efficiently and effectively.

Thanks for the invite ............................ agreed with the answers Mr. Shahul Hameed Mohammed

Thanks
I fully agree with Mr viayapuri sir

I prefer to leave answers to Experts. Thanks for Your kind Invitation.

Rationale for human resource management evaluation The notion that HR function should move beyond its administrative and controlling roles and value has been popular in the US management for long time. Druker, theAmerican management guru, suggested , for example that HR Department should behave differently and demonstrate its strategic capabilities , needing itself away from concern with the cost of employees to concern with their yield . According to Phllips (1999) , there are seven points in the management thinking and practices that changed the role HR. Organisational change Flexibility and productivity improvements The adoption of HR strategies The increased importance of human capital Increased accountability Partnership relationships The growing use of HR information systems HR Strategy - HR strategies are here taken to mean the patterns of decision regarding HR policies and practices that are used by management to design work and select , train, develop, appraise, motivate and control workers Resource based model of HR Strategy - Barney argues that four characteristics of resources and capabilities - value, rarity, inimitability and non- substitutability- are important in sustaining competitive advantage. From this perspective, collective learning in the workplace on the part of managers and non managers, basically on how to coordinate workers diverse knowledge and skills and integrate diverse information technology , is strategic asset that rivals find to difficult to replicate. Figure 3summarizes the relationship between resources and capabilities strategies and sustain competitive advantage Figure: The relationship between resource endowments, strategies and sustained competitive advantage.. SHAPE Firm's resources and capabilities Value Rarity Inimitability Non-substitutability Strategies Sustained competitive advantage Source: Barney (1991)

Thanks Ms Ghada for invitation
I agree with the answers given by colleagues Shahul and wealid Ismail

Thanks for invitation
Agree with Ghada's answwer

Thanks for invite;
Harvard Model present four HR policy area of HR Flows, Reward System, employee influence and work system reveals for their managers to strongly comitment to attain organization goals by strategicaly and systematical control of employees.



